

Regulation Z also provides examples of charges that are not considered finance charges, like annual fees or late fees on a credit card, taxes, registration fees or license fees. Required insurance premiums, like private mortgage insurance (PMI).Appraisal fees, origination fees and credit report fees.Service fees, transaction fees, activity or carrying charges.Regulation Z provides examples of finance charges, including : According to the Federal Reserve, a finance charge doesn’t include every cost involved with obtaining consumer credit. What Does a Finance Charge Include?Ĭoming up with the exact dollar amount of a finance charge can be complicated. Finance charge disclosures are designed to help consumers know how much a financial product will cost them.īecause the disclosures are standardized, borrowers can make apples-to-apples comparisons when they’re searching for the best deal on financing. TILA also makes it easier for consumers to compare credit by standardizing terminology and the way rates are disclosed. One of the primary purposes of TILA is to protect consumers as they work with creditors and lenders. TILA was passed in 1968 and was implemented by the Federal Reserve Board’s Regulation Z the following year. This requirement is thanks to a federal law known as the Truth in Lending Act (TILA). Lenders and card issuers have to disclose finance charges in writing before you can borrow money. Finance charges and the Truth in Lending Act If you’re trying to figure out which costs are included with finance charges, here’s a helpful trick: Finance charges typically represent costs you wouldn’t incur if you were paying with cash instead of credit. They can include a combination of interest and fees. What Is a Finance Charge?Ī finance charge – which can be a flat fee or a percentage – is the amount of money you pay to borrow funds from a lender, credit card issuer or other financial institution.Ī common misconception is that a finance charge means interest. Let’s explore finance charges, how they work – and how you can avoid them. Most importantly, you’ll need to figure out exactly how much a loan or other financial product will cost. Whether you’re taking out a mortgage, applying for an auto loan or opening a new credit card, it’s essential to know what to expect upfront. Importantly, borrowers can get liquidated if the asset they borrow increases in value and becomes more valuable than the posted collateral.There’s a lot of information to gather before you can borrow money. Users who lend assets to the protocol, can take out a loan in any other cryptocurrency that Compound offers, up to the amount of collateral posted. The more liquidity in a market, the lower the interest rate. They are allowed to borrow cryptocurrencies supported by Compound at a percentage of the posted value.Ĭompound rewards lenders with COMP tokens based on the amount of cTokens held in their wallet based on a varying interest rate dependent on the available supply of that asset. Borrowers – Anyone who posts collateral on Compound in the form of a cryptocurrency.Lenders – Anyone wishing to lend a cryptocurrency on Compound can send their tokens to an Ethereum address controlled by Compound to earn interest.The two main users of the platform include: As of 2020, over $500 million in assets were locked in the Compound protocol, according to the data site DeFi Pulse.Ĭompound connects lenders and borrowers using a combination of smart contracts running on Ethereum and incentives paid in cryptocurrency. While complex, the model has so far proved adept at attracting users and encouraging other DeFi cryptocurrencies to adopt its model. Every time a user interacts with a Compound market (by borrowing, withdrawing or repaying the asset), they are rewarded with additional COMP tokens. To incentivize this activity, Compound uses another cryptocurrency native to its service, called COMP. This entire process is automatic and handled by the Compound code, meaning lenders can withdraw deposits at any time. Examples of cTokens include cETH, cBAT and cDAI.Įach cToken can be transferred or traded without restriction, but it is only redeemable for the cryptocurrency initially locked in the protocol.
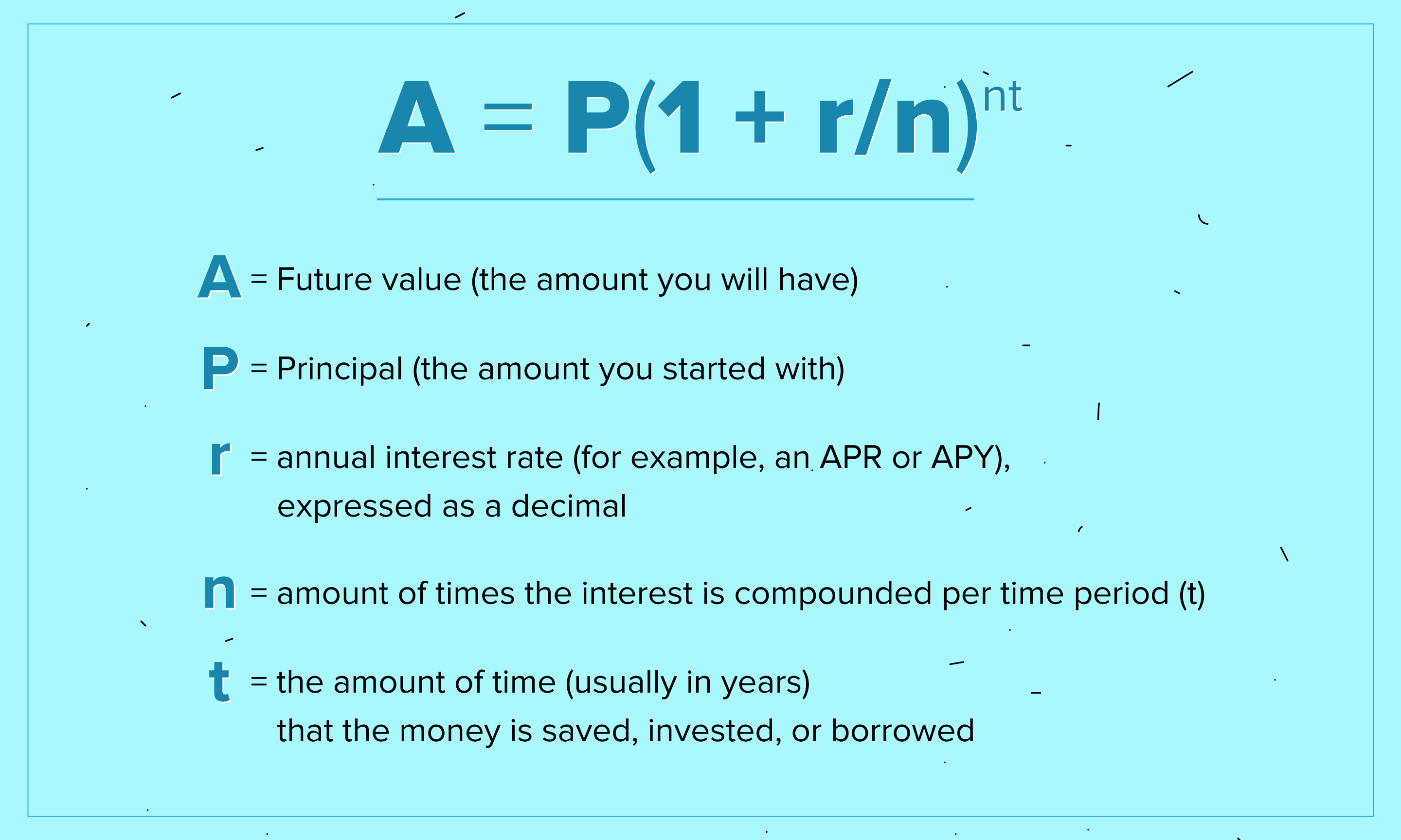
Once a deposit is made, Compound awards a new cryptocurrency called a cToken (which represents the deposit) to the lender. Lenders then earn interest on the assets they deposit. Put simply, Compound allows users to deposit cryptocurrency into lending pools for access by borrowers. One of an emerging number of decentralized finance ( DeFi) protocols, Compound uses multiple crypto assets to provide this service, enabling the lending and borrowing required without a financial intermediary like a bank.
Compound define finance software#
Compound is a software running on Ethereum that aims to incentivize a distributed network of computers to operate a traditional money market.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
